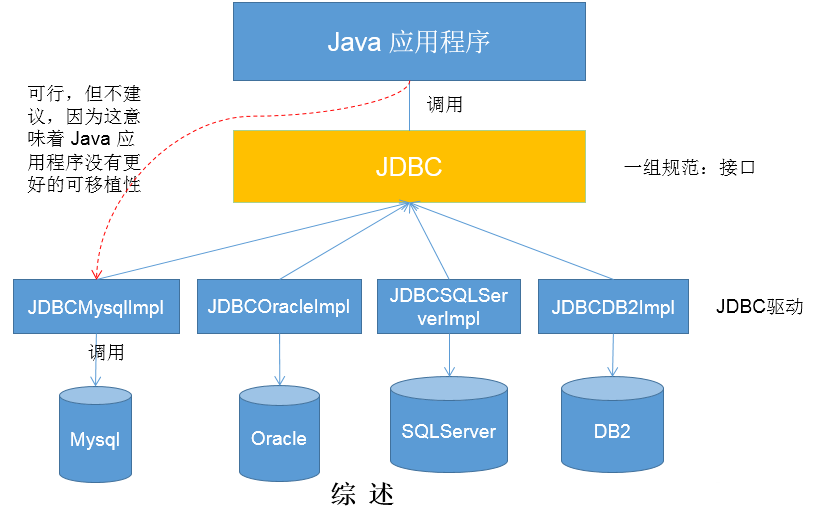
JDBC概述 软件架构:B/S (Browser Server) 、 C/S (Client Server)
概念:JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)是一个独立于特定数据库管理系统、通用的SQL数据库存取和操作的公共接口 (一组API),
定义了用来访问数据库的标准Java类库(java.sql,javax.sql )。
JDBC体系 JDBC接口(API):
面向应用的API :Java API,抽象接口,供应用程序开发人员使用(连接数据库,执行SQL语句,获得结果)。面向数据库的API :Java Driver API,供开发商开发数据库驱动程序用。
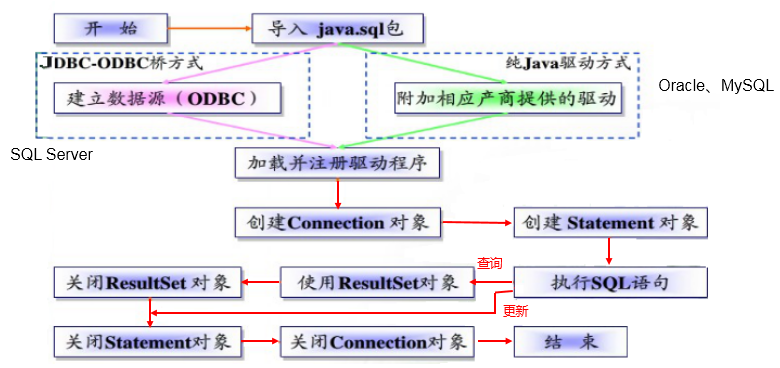
JDBC 连接步骤
获取数据库连接
Driver接口实现类
常用方式的好处是
①实现了代码和数据的分离,不需要以硬编码的方式一起存在,在更改连接数据库的方面更加方便和安全
②在修改配置文件的时候可以避免程序的重新打包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 @Test public void jdbc_Connection5 () throws Exception { InputStream in = ConnectionTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties" ); Properties p = new Properties (); p.load(in); String user = p.getProperty("user" ); String paw = p.getProperty("password" ); String url = p.getProperty("url" ); String driver = p.getProperty("driverClass" ); Class.forName(driver); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, paw, user); System.out.println(connection); } @Test public void jdbc_Connection () throws SQLException { Driver driver = new com .mysql.jdbc.Driver(); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8" ; Properties p = new Properties (); p.setProperty("user" ,"root" ); p.setProperty("password" ,"root" ); Connection connect = driver.connect(url, p); System.out.println(connect); } @Test public void jdbc_Connection2 () throws Exception { Class<?> a = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Driver driver = (Driver) a.newInstance(); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8" ; Properties p = new Properties (); p.setProperty("user" ,"root" ); p.setProperty("password" ,"root" ); Connection connect = driver.connect(url, p); System.out.println(connect); } @Test public void jdbc_Connection3 () throws Exception { Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Driver driver = (Driver) aClass.newInstance(); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8" ; String user = "root" ; String paw = "root" ; DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, paw); System.out.println(connection); } @Test public void jdbc_Connection4 () throws Exception { String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8" ; String user = "root" ; String paw = "root" ; Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, paw); System.out.println(connection);
访问和操作数据库 数据库连接被用于向数据库服务器发送命令和 SQL 语句,并接受数据库服务器返回的结果。其实一个数据库连接就是一个Socket连接。
在 java.sql 包中有 3 个接口分别定义了对数据库的调用的不同方式:
Statement:用于执行静态 SQL 语句并返回它所生成结果的对象。
PrepatedStatement:SQL 语句被预编译并存储在此对象中,可以使用此对象多次高效地执行该语句。
CallableStatement:用于执行 SQL 存储过程
Statement的弊端:需要拼写sql语句,并且存在sql注入的问题
关于PrepatedStatement的使用 作为Statement的子接口,解决了Statement的弊端,还可以操作Blob的数据,而Statement不行
此外,还可以实现更高效的批量操作
使用PreparedStatement实现增、删、改操作的通用操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 public void update (String sql,Object ... args) { Connection connection = null ; PreparedStatement ps = null ; try { connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i+1 ,args[i]); } ps.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,ps); } public class JDBCUtils { public static Connection getConnection () throws Exception { InputStream in = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties" ); Properties p = new Properties (); p.load(in); String user = p.getProperty("user" ); String paw = p.getProperty("password" ); String url = p.getProperty("url" ); String driver = p.getProperty("driverClass" ); Class.forName(driver); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, paw, user); return connection; } public static void closeResource (Connection connection, PreparedStatement ps) { try { if (ps !=null ) ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (connection!=null ) connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
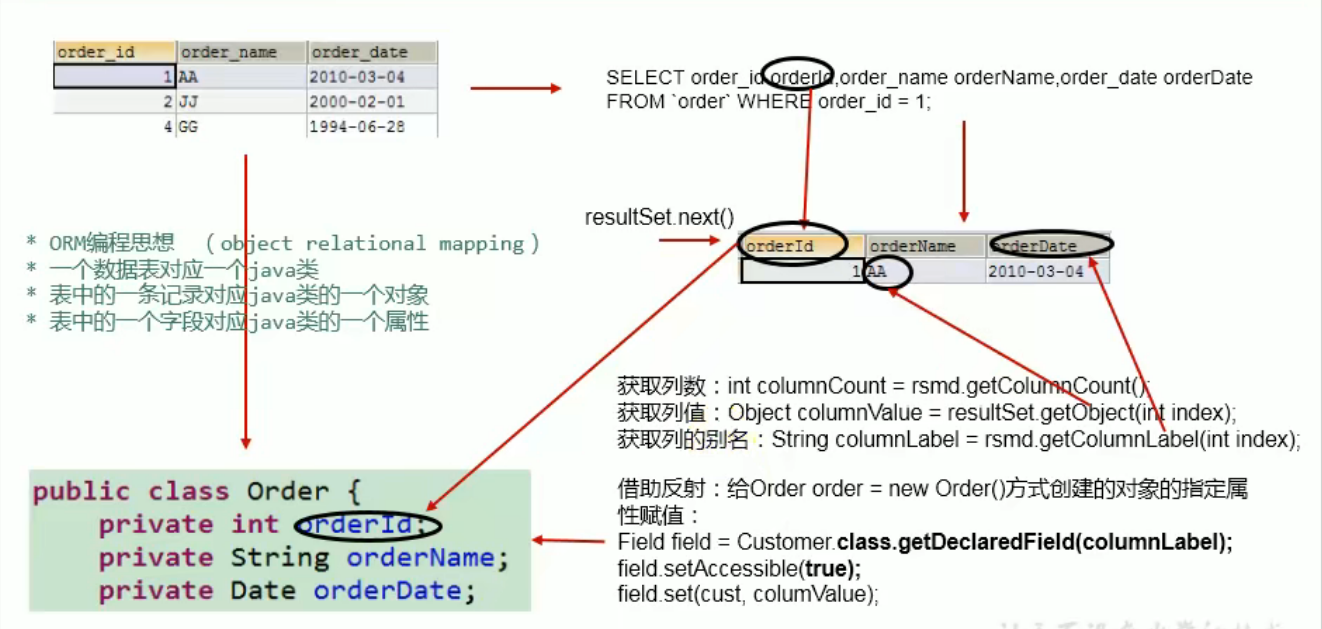
使用PreparedStatement实现查询具体表的通用操作
针对表的字段名和属性名不相同的情况下:
①必须声明sql时,使用类的属性名来命名字段的别名
②使用ResultSetMetaData时,需要使用getColumnLabel()来替换getColumnName()获取列的别名
③如果sql中没有给字段起别名,getColumnLabel()获取的是原列名
④当数据表中的字段名和对应的类属性名不同式,需要在sql语句中给字段名添加 以类属性名 起名的列名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 ublic Customers selectForCustomers (String sql,Object ... args) throws Exception { Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i+1 ,args[i]); } ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); if (rs.next()){ Customers cust = new Customers (); for (int i = 0 ; i < columnCount; i++) { Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i + 1 ); String ColumnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1 ); Field field = Customers.class.getDeclaredField(ColumnLabel); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(cust,columnValue); } return cust; } JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,ps,rs); return null ; }
使用PreparedStatement实现不同表的查询操作
PS:以下为课件提供的,自己按照思路重写的放在了prestament_differen_table包下,忘记了可以看此包下的写法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 / / 通用的针对于不同表的查询:返回一个对象 (version 1.0 ) public < T> T getInstance(Class< T> clazz, String sql , Object... args) { Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement ps = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { / / 1. 获取数据库连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); / / 2. 预编译sql 语句,得到PreparedStatement对象 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql ); / / 3. 填充占位符 for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i+ + ) { ps.setObject(i + 1 , args[i]); } / / 4. 执行executeQuery(),得到结果集:ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); / / 5. 得到结果集的元数据:ResultSetMetaData ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); / / 6.1 通过ResultSetMetaData得到columnCount,columnLabel;通过ResultSet得到列值 int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); if (rs.next()) { T t = clazz.newInstance(); for (int i = 0 ; i < columnCount; i+ + ) {/ / 遍历每一个列 / / 获取列值 Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1 ); / / 获取列的别名:列的别名,使用类的属性名充当 String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1 ); / / 6.2 使用反射,给对象的相应属性赋值 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(t, columnVal); } return t; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { / / 7. 关闭资源 JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs); } return null ; }
Java与SQL对应数据类型转换
Java类型
SQL类型
boolean
BIT
byte
TINYINT
short
SMALLINT
int
INTEGER
long
BIGINT
String
CHAR,VARCHAR,LONGVARCHAR
byte array
BINARY , VAR BINARY
java.sql.Date
DATE
java.sql.Time
TIME
java.sql.Timestamp
TIMESTAMP
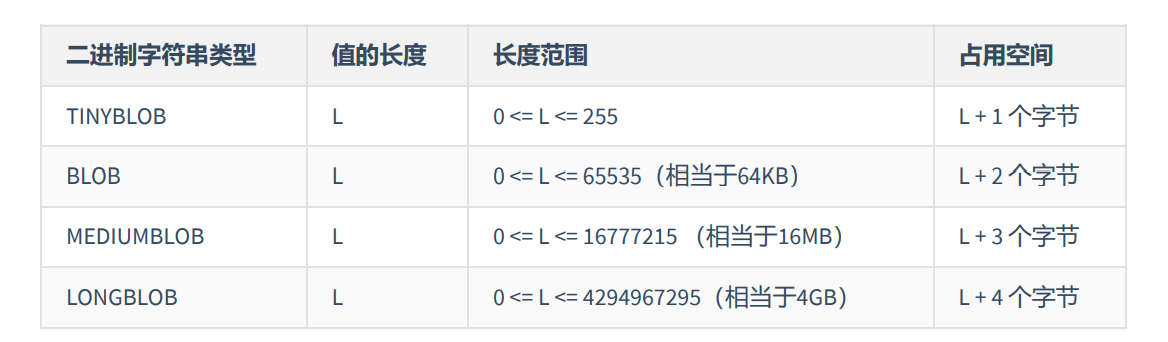
操作Blob类型的字段 插入BLOB类型的数据必须使用PreparedStatement ,因为BLOB类型的数据无法使用字符串拼接写的。
需要注意的是:如果存储的文件过大,数据库的性能会下降。
如果在指定了相关的Blob类型以后,还报错:xxx too large,那么在mysql的安装目录下,找my.ini文件加上如下的配置参数: max_allowed_packet=16M 。同时注意:修改了my.ini文件之后,需要重新启动mysql服务。
向数据库customers表中插入blob类型的字段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth,photo) values(?,?,?,?)" ;PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);ps.setObject(1 ,"测试" ); ps.setObject(2 ,"test@qq.com" ); ps.setObject(3 ,"2000-10-12" ); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream ("src\\test.jpg" );ps.setBlob(4 ,in); ps.execute(); JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,ps);
查询数据库customers表中blob类型的字段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth,photo from customers where id = ?" ; PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setObject(1 ,20 ); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); InputStream bs = null ; FileOutputStream output = null ; if (rs.next()){ int id = rs.getInt("id" ); String email = rs.getString("email" ); String name = rs.getString("name" ); Date birth = rs.getDate("birth" ); Customers customers = new Customers (id, name, email, birth); System.out.println(customers); Blob photo = rs.getBlob("photo" ); bs = photo.getBinaryStream(); output = new FileOutputStream (new File ("test1.jpg" )); byte [] b = new byte [1024 ]; int len; while ((len = bs.read(b)) != -1 ){ output.write(b,0 ,len); } } bs.close(); output.close(); JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,ps,rs);
批量插入 JDBC的批量处理语句包括下面三个方法:
addBatch(String):添加需要批量处理的SQL语句或是参数; executeBatch():执行批量处理语句; clearBatch():清空缓存的数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 @Test public void testFnally () throws Exception{ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); connection.setAutoCommit(false ); String sql = "insert into goods(name) values(?)" ; PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 1 ; i <= 100000 ; i++) { ps.setObject(1 ,"name" + i); ps.addBatch(); if (i % 500 == 0 ){ ps.executeBatch(); ps.clearBatch(); } } connection.commit(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("所花的时间为" + (end - start)); JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,ps); }
PreparedStatement 与 Statement的区别
数据库事务
事务:一组逻辑操作单元使得数据从一种状态变为另一种状态
事务处理的原则:要么成功,所有的操作都被提交(commit);要么失败,所有的操作都被回滚(rollback)
在断开连接的时候也会自动提交已经修改的数据,即使设置了set autocommit = false;
java程序中让多个sql语句作为一个事务执行:
①调用 Connection 对象的 setAutoCommit(false); 以取消自动提交事务
②成功执行后,调用 commit(); 方法提交事务
③在出现异常时,调用 rollback(); 方法回滚事务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public void testTransaction () { Connection conn = null ; try { conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); conn.setAutoCommit(false ); String sql1 = "update user_table set balance = balance - 100 where user = ?" ; update(conn, sql1, "AA" ); String sql2 = "update user_table set balance = balance + 100 where user = ?" ; update(conn, sql2, "BB" ); conn.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } finally { try { conn.setAutoCommit(true ); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null , null ); } return 0 ; }
对数据库的操作方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public void update (Connection conn ,String sql, Object... args) { PreparedStatement ps = null ; try { ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i + 1 , args[i]); } ps.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(null , ps); } }
事务的ACID属性
原子性(Atomicity)
原子性是指事务是一个不可分割的单位,对事务的操作要么都成功,要么都不成功
一致性(Consistency)
事务必须让数据库从一个一致的状态变为另一个一致的状态
隔离性(Isolation)
隔离性是指一个事务的执行不能被其他的事务干扰,即一个事务其内部的操作对于其他此刻并发的事务来说是隔离的,各个事务之间相互不影响
持久性(Durability)
持久性是指一个事务被提交之后,对数据库的修改是永久性的。数据库的任何改变都不能影响它
数据库并发问题
脏读 : 对于两个事务 T1, T2, T1 读取了已经被 T2 更新但还没有被提交 的字段。之后, 若 T2 回滚, T1读取的内容就是临时且无效的。
不可重复读 : 对于两个事务T1, T2, T1 读取了一个字段, 然后 T2 更新 了该字段。之后, T1再次读取同一个字段, 值就不同了。
幻读 : 对于两个事务T1, T2, T1 从一个表中读取了一个字段, 然后 T2 在该表中插入 了一些新的行。之后, 如果 T1 再次读取同一个表, 就会多出几行。
数据库事务的隔离性 : 数据库系统必须具有隔离并发运行各个事务的能力, 使它们不会相互影响, 避免各种并发问题。
数据库隔离级别 一个事务与其他事务隔离的程度称为隔离级别,隔离级别越高, 数据一致性就越好, 但并发性越弱。
隔离级别1啥也没解决,级别2解决了脏读问题,级别3解决了脏读和不可重复读的问题,级别4解决了脏读和不可重复读及幻读问题
MySQL 支持这 4 种隔离级别,默认隔离级别为REPEATBLE READ 而在Oracle 中仅支持其中 2 种,分别为READ COMMITED, SERIALIZABLE,默认隔离级别为READ COMMITED
DAO及相关实现类 DAO.java 封装了整体常用的增删改查的方法体
静态代码块内的操作想法是通过this获取所属类再获取所属类的父类,在强转成带泛型的父类,在获取泛型数组,再取第一个泛型类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 public abstract class Dao <T> { private Class<T> clazz = null ; { Type genericSuperclass = this .getClass().getGenericSuperclass(); ParameterizedType parameterizedType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass; Type[] actualTypeArguments = parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments(); clazz = (Class<T>) actualTypeArguments[0 ]; } public int update (Connection conn,String sql,Object... args) { PreparedStatement ps = null ; try { ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i + 1 , args[i]); } return ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(null , ps); } return 0 ; } public T getInstance (Connection conn,String sql, Object... args) { PreparedStatement ps = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i + 1 , args[i]); } rs = ps.executeQuery(); ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); if (rs.next()) { T t = clazz.newInstance(); for (int i = 0 ; i < columnCount; i++) { Object columValue = rs.getObject(i + 1 ); String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1 ); Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(t, columValue); } return t; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(null , ps, rs); } return null ; } public List<T> getListQuery (Connection connection,String sql, Object ... args) { PreparedStatement ps = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i+1 ,args[i]); } rs = ps.executeQuery(); ResultSetMetaData rsdm = rs.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsdm.getColumnCount(); ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList <>(); while (rs.next()){ T t = clazz.newInstance(); for (int i = 0 ; i < columnCount; i++) { Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i + 1 ); String columnLabel = rsdm.getColumnLabel(i + 1 ); Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(t,columnValue); } list.add(t); } return list; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(null ,ps,rs); } return null ; } public <E> E getValue (Connection connection,String sql,Object ... args) { PreparedStatement ps = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i+1 ,args[i]); } rs = ps.executeQuery(); if (rs.next()){ return (E) rs.getObject(1 ); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(null ,ps,rs); } return null ; } }
CustomersDao.java 作为接口出现,封装了对customer表的抽象方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public interface CustomersDao { void insert (Connection connection,Customers cust) ; void deleteById (Connection connection,int id) ; void update (Connection connection,Customers cust) ; Customers getById (Connection connection,int id) ; List<Customers> getAll (Connection connection) ; Long getCount (Connection connection) ; Date getMaxBirth (Connection connection) ; }
CustomersDaoImpl.java 作为DAO的子类,实现了CustomersDao,主要通过调用DAO的基本方法填入相关参数实现对表的修改
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public class CustomersDaoImpl extends Dao <Customers> implements CustomersDao { @Override public void insert (Connection connection, Customers cust) { String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth) values(?,?,?)" ; update(connection,sql,cust.getName(),cust.getEmail(),cust.getBirth()); } @Override public void deleteById (Connection connection, int id) { String sql = "delete from customers where id = ?" ; update(connection,sql,id); } @Override public void update (Connection connection, Customers cust) { String sql = "update customers set name = ?,email = ?,birth = ? where id = ?" ; update(connection,sql,cust.getName(),cust.getEmail(),cust.getBirth(),cust.getId()); } @Override public Customers getById (Connection connection, int id) { String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?" ; Customers customers = getInstance(connection,sql,id); return customers; } @Override public List<Customers> getAll (Connection connection) { String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers" ; List<Customers> list = getListQuery(connection,sql); return list; } @Override public Long getCount (Connection connection) { String sql = "select count(*) from customers" ; return getValue(connection, sql); } @Override public Date getMaxBirth (Connection connection) { String sql = "select max(birth) from customers" ; return getValue(connection,sql); } }
对CustomersDaoImpl.java的测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 CustomersDaoImpl dao = new CustomersDaoImpl (); @Test public void insert () { Connection connection = null ; try { connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); Customers cust = new Customers (1 , "张扬" , "test@qq.com" , new Date (15565565534L )); dao.insert(connection,cust); System.out.println("添加成功" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,null ); } }
数据库连接池 java内存泄漏:即堆空间中有对象没有被回收
好处是减低资源消耗,可以重复使用,便于连接的管理。提高程序响应的速度
数据库连接池 负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是重新建立一个 。(与线程池思想相似。)
使用第三方的创建数据库连接池都需要导入相应的jar包和创建填写相应的配置文件
JDBC 的数据库连接池使用 javax.sql.DataSource 来表示 ,DataSource 只是一个接口,该接口通常由服务器 (Weblogic, WebSphere, Tomcat)提供实现,
也有一些开源组织提供实现:
C3P0 速度较快,但不稳定
1 2 3 4 5 6 private static Datesource source = new ComboPooledDataSource ("C3P0" ); public Connection test2 () throws SQLException { Connection connection = cpds.getConnection(); return connection; }
src下的配置文件为:【c3p0-config.xml】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 //配置文件 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <c3p0-config > <named-config name ="C3P0" > <property name ="driverClass" > com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property > <property name ="jdbcUrl" > jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8& useSSL=false& serverTimezone=UTC& rewriteBatchedStatements=true</property > <property name ="user" > root</property > <property name ="password" > root</property > <property name ="acquireIncrement" > 5</property > <property name ="initialPoolSize" > 10</property > <property name ="minPoolSize" > 10</property > <property name ="maxPoolSize" > 100</property > <property name ="maxStatements" > 50</property > <property name ="maxStatementsPerConnection" > 2</property > </named-config > </c3p0-config >
DPCP 速度较慢,但比较稳定
需要依赖两个jar包才能实现创建数据库连接池
Commons-dbcp.jar:连接池的实现
Commons-pool.jar:连接池实现的依赖库
Tomcat 的连接池正是采用该连接池来实现的 。
属性
默认值
说明
initialSize
0
连接池启动时创建的初始化连接数量
maxActive
8
连接池中可同时连接的最大的连接数
maxIdle
8
连接池中最大的空闲的连接数,超过的空闲连接将被释放,如果设置为负数表示不限制
minIdle
0
连接池中最小的空闲的连接数,低于这个数量会被创建新的连接。该参数越接近maxIdle,性能越好,因为连接的创建和销毁,都是需要消耗资源的;但是不能太大。
maxWait
无限制
最大等待时间,当没有可用连接时,连接池等待连接释放的最大时间,超过该时间限制会抛出异常,如果设置-1表示无限等待
poolPreparedStatements
false
开启池的Statement是否prepared
maxOpenPreparedStatements
无限制
开启池的prepared 后的同时最大连接数
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis
连接池中连接,在时间段内一直空闲, 被逐出连接池的时间
removeAbandonedTimeout
300
超过时间限制,回收没有用(废弃)的连接
removeAbandoned
false
超过removeAbandonedTimeout时间后,是否进 行没用连接(废弃)的回收
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 private static DataSource source; static { try { Properties pro = new Properties (); InputStream in = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dpcp.properties" ); pro.load(in); source = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static Connection getConnection1 () throws Exception { Connection connection = source.getConnection(); return connection; }
//配置文件
1 2 3 4 username =root password =root url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&rewriteBatchedStatements=true driverClassName =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
Druid(德鲁伊) 目前最为推荐的数据库连接池创建方式
source1 = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private static DataSource source1; static { try { Properties pro = new Properties (); InputStream in = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties" ); pro.load(in); source1 = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static Connection getConnection3 () throws SQLException { Connection connection = source1.getConnection(); return connection; }
//配置文件
1 2 3 4 url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&rewriteBatchedStatements=true username =root password =root driverClassName =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
配置 缺省 说明
name
配置这个属性的意义在于,如果存在多个数据源,监控的时候可以通过名字来区分开来。 如果没有配置,将会生成一个名字,格式是:”DataSource-” + System.identityHashCode(this)
url
连接数据库的url,不同数据库不一样。例如:mysql : jdbc:mysql://10.20.153.104:3306/druid2 oracle : jdbc:oracle:thin:@10.20.149.85:1521:ocnauto
username
连接数据库的用户名
password
连接数据库的密码。如果你不希望密码直接写在配置文件中,可以使用ConfigFilter。详细看这里:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/wiki/%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8ConfigFilter
driverClassName
根据url自动识别 这一项可配可不配,如果不配置druid会根据url自动识别dbType,然后选择相应的driverClassName(建议配置下)
initialSize
0
初始化时建立物理连接的个数。初始化发生在显示调用init方法,或者第一次getConnection时
maxActive
8
最大连接池数量
maxIdle
8
已经不再使用,配置了也没效果
minIdle
最小连接池数量
maxWait
获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降,如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。
poolPreparedStatements
false
是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。在mysql下建议关闭。
maxOpenPreparedStatements
-1
要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
validationQuery
用来检测连接是否有效的sql,要求是一个查询语句。如果validationQuery为null,testOnBorrow、testOnReturn、testWhileIdle都不会其作用。
testOnBorrow
true
申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。
testOnReturn
false
归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能
testWhileIdle
false
建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis
有两个含义: 1)Destroy线程会检测连接的间隔时间2)testWhileIdle的判断依据,详细看testWhileIdle属性的说明
numTestsPerEvictionRun
不再使用,一个DruidDataSource只支持一个EvictionRun
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis
connectionInitSqls
物理连接初始化的时候执行的sql
exceptionSorter
根据dbType自动识别 当数据库抛出一些不可恢复的异常时,抛弃连接
filters
属性类型是字符串,通过别名的方式配置扩展插件,常用的插件有: 监控统计用的filter:stat日志用的filter:log4j防御sql注入的filter:wall
proxyFilters
类型是List,如果同时配置了filters和proxyFilters,是组合关系,并非替换关系
Apache-DBUtils实现CRUD操作 commons-dbutils 是 Apache 组织提供的一个开源 JDBC工具类库,它是对JDBC的简单封装,学习成本极低,并且使用dbutils能极大简化jdbc编码的工作量,同时也不会影响程序的性能。
主要使用 DbUtils
DbUtils :提供如关闭连接、装载JDBC驱动程序等常规工作的工具类,里面的所有方法都是静态的。主要方法如下:
public static void close(…) throws java.sql.SQLException : DbUtils类提供了三个重载的关闭方法。这些方法检查所提供的参数是不是NULL,如果不是的话,它们就关闭Connection、Statement和ResultSet。public static void closeQuietly(…): 这一类方法不仅能在Connection、Statement和ResultSet为NULL情况下避免关闭,还能隐藏一些在程序中抛出的SQLEeception。
public static void commitAndClose(Connection conn)throws SQLException: 用来提交连接的事务,然后关闭连接
public static void commitAndCloseQuietly(Connection conn): 用来提交连接,然后关闭连接,并且在关闭连接时不抛出SQL异常。
public static void rollback(Connection conn)throws SQLException:允许conn为null,因为方法内部做了判断
public static void rollbackAndClose(Connection conn)throws SQLException
rollbackAndCloseQuietly(Connection)
public static boolean loadDriver(java.lang.String driverClassName):这一方装载并注册JDBC驱动程序,如果成功就返回true。使用该方法,你不需要捕捉这个异常ClassNotFoundException。
QueryRunner类
该类简单化了SQL查询,它与ResultSetHandler组合在一起使用可以完成大部分的数据库操作,能够大大减少编码量。 QueryRunner类提供了两个构造器:
默认的构造器
需要一个 javax.sql.DataSource 来作参数的构造器
QueryRunner类的主要方法:
更新
public int update(Connection conn, String sql, Object… params) throws SQLException:用来执行一个更新(插入、更新或删除)操作。
插入
public T insert(Connection conn,String sql,ResultSetHandler rsh, Object… params) throws SQLException:只支持INSERT语句,其中 rsh - The handler used to create the result object from the ResultSet of auto-generated keys. 返回值: An object generated by the handler.即自动生成的键值
批处理
public int[] batch(Connection conn,String sql,Object[][] params)throws SQLException: INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE语句
public T insertBatch(Connection conn,String sql,ResultSetHandler rsh,Object[][] params)throws SQLException:只支持INSERT语句
查询
public Object query(Connection conn, String sql, ResultSetHandler rsh,Object… params) throws SQLException:执行一个查询操作,在这个查询中,对象数组中的每个元素值被用来作为查询语句的置换参数。该方法会自行处理 PreparedStatement 和 ResultSet 的创建和关闭。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 public class QueryRunnerTest { @Test public void test () { Connection connection = null ; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner (); connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth) values(?,?,?)" ; int update = runner.update(connection, sql, "tt" , "tt@gmail.com" , new Date (564849879844L )); System.out.println("更新了" + update + "条数据" ); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,null ); } } @Test public void testQuery1 () { Connection connection3 = null ; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner (); connection3 = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?" ; BeanHandler<Customers> handler = new BeanHandler <>(Customers.class); Customers query = runner.query(connection3, sql, handler, 23 ); System.out.println(query); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection3,null ); } } @Test public void testQuery2 () { Connection connection3 = null ; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner (); connection3 = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id < ?" ; BeanListHandler<Customers> handler = new BeanListHandler <>(Customers.class); List<Customers> query = runner.query(connection3, sql, handler, 10 ); query.forEach(System.out :: println); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection3,null ); } } @Test public void testQuery3 () { Connection connection3 = null ; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner (); connection3 = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?" ; MapHandler mapHandler = new MapHandler (); Map<String, Object> query = runner.query(connection3, sql, mapHandler, 10 ); System.out.println(query); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection3,null ); } } @Test public void testQuery4 () { Connection connection3 = null ; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner (); connection3 = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id < ?" ; MapListHandler mapListHandler = new MapListHandler (); List<Map<String, Object>> query = runner.query(connection3, sql, mapListHandler, 10 ); query.forEach(System.out :: println); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection3,null ); } } @Test public void testQuery5 () { Connection connection3 = null ; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner (); connection3 = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select count(*) from customers" ; ScalarHandler scalarHandler = new ScalarHandler (); long count = (long ) runner.query(connection3, sql, scalarHandler); System.out.println(count); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection3,null ); } }
总结 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 总结 @Test public void testUpdateWithTx () { Connection conn = null ; try { conn.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } }finally { } }